Tag: agarose
Agarose
Agarose is a useful matrix for a number of analytical and preparative techniques including gel electrophoresis, chromatography, and support matrix to immobilize enzymes and cells. Agarose is available in a variety of forms, which differ in physical properties. The two most common agarose are standard agarose and low melting agarose. Standard agarose is most commonly used for analysis of DNA and RNA. Low melting agarose is often used for preparative purposes such as elution of DNA fragments and complexes.
Protocol: Running DNA Samples in Agarose Gel
Agarose gel is placed in an electrophoresis tank filled with an electrophoresis buffer. DNA samples are mixed with DNA loading dye and loaded onto the wells of agarose gel. Electrophoresis apparatus is connected to electric supply and electrophoresis is performed at constant voltage until the desired separation among DNA fragments is achieved. After the run is over, gel is analyzed using UV-transilluminator or Gel Doc system.
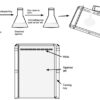
Protocol: Preparation of Agarose Gel for DNA Analysis
Agarose Gel is a gelatin-like slab, which contains small wells for loading DNA samples. It is prepared by melting agarose in a suitable electrophoresis buffer. Molten agarose is then poured into a specialized tray (casting tray), which controls the size and shape of the gel. The comb is used to create wells in agarose gel.