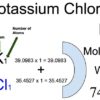
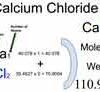
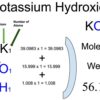
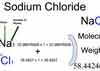
Category: Laboratory Calculations
Preparation of 1M Hydrochloric Acid From Concentrated Stock Solution (37%, w/w)
A 37% (w/w) hydrochloric acid can be purchased from several suppliers. It is a clear colorless liquid and can be diluted to prepare solutions of known concentrations. Remember that the molarity of hydrochloric acid is equal to the normality of the solution, which means 1M solution is also a 1N solution. Here we describe a procedure to prepare 1M hydrochloric acid solution by diluting a 37% (w/w) concentrated hydrochloric acid solution.